



We have touched upon the Japanese side being challenged with internal buy-in/alignment for Australia, and the Australian side on the “customized approach” to Japan or Japanese corporates. While these issues can be anticipated and planned for, unexpected situations always arise. Hence, the actual engagement will become a valuable experience for understanding each other. This Part III (the final part in the series) intends to put a spotlight on how Japanese corporations can engage with Australian universities and research institutes. These institutions offer a wealth of untapped potential and represent a rich source of capabilities Japanese corporations can leverage off, and frankly less explored at this stage.
The wider objective of this piece is our contribution to a conversation about increasing the A-J innovation success cases in the Australia-Japan corridor. Specifically, IGPI shares some of its observations of how Japanese corporates can engage or partner with Australian universities and research institutes – these could be in the forms of straightforward research relationships all the way to commercialization initiatives.
Throughout the article series, we have touched on the changing nature of “What” and “Who” Japanese corporations are collaborating with in the Australia-Japan corridor. We explored the capabilities of the broader Australian innovation ecosystem, including universities and research institutes.
However, we also highlighted that both Japanese and Australian sides need to prepare internally before engaging. For Japanese corporations, this involves internal alignment between headquarters and the local arm. For Australians, it means developing a customized Japan strategy to understand and overcome cultural or communication barriers.
You can find Part I can be found here and Part II here.
The next question is “how,” or in other words, the “actions” to take for collaboration.
It is first important to note that it is common for Australian universities to have a dedicated department for managing industry collaboration and IP-related matters (e.g. commercialization). These departments are generally known as “Technology Transfer Offices” or TTOs1.
TTO is a general term, and some universities might call it an “Industry Engagement Office” or something similar. TTOs are a crucial point of engagement for any industry partner, regardless of whether they have existing connections with university faculty. This is because the university’s IP management and contractual matters will ultimately be handled by the TTO. Therefore, establishing a holistic relationship with the university early on is important and beneficial.
From the Australian perspective, identifying the right contact within a Japanese corporation is essential. However, this is easier said than done since, unlike Australian universities with their standardized TTO function, Japanese corporate structures vary significantly. To get started, having a Japanese engagement specialist is helpful. If this expertise is not accessible internally, then engaging with government bodies (like Austrade in Japan) or ecosystem participants (like IGPI) can be a strong starting point for your Australia-Japan innovation journey.
Once you know who to contact, the next step is exploring engagement and partnership options. Here are some collaboration methods Japanese corporations and Australian universities can potentially explore (but not limited to):
2.1. Example of Mode of Collab. # 1: Contract Research
Contract research offers a tailored approach for Japanese corporations to access expertise from Australian universities on specific research topics. This could include, consulting, evaluations, lab services, or independent research projects2. The scope is flexible and can range from simple research outsourcing to joint research projects led or supported by the university. However, contract research is generally considered a transactional engagement rather than a long-term partnership, though it can be a stepping stone. It’s a valuable way for Japanese corporations in Australia to gain first-hand experience with a university’s research capabilities.
2.2. Example of Mode of Collab. # 2: Center of Excellence (CoE)
Center of Excellence (CoE) is a generic term referring to hubs that have specialized units (or individuals, or even collaborations between organizations) focused on a particular area of expertise3. While not exclusively research-focused, CoEs can be instrumental in driving business or industry transformation.
There are already examples of CoEs in Australia with Japanese participants.
| CoE | Brief Example |
|---|---|
| ARC Centre of Excellence in Quantum Biotechnology x Olympus | The Arc Centre of Excellence in Quantum Biotechnology’s focus is partnering with industry and government to seek to drive fundamental understanding and innovation across manufacturing, clean energy, agriculture, health and national security4. |
Unlike contract research, a CoE represents a deeper commercial and technical collaboration on a focus area between the partners.
2.3. Example of Mode of Collab. # 3: Intellectual Property (IP) utilisation
Compared to the previous examples, utilizing intellectual property (IP) offers a more direct and relatively immediate path to commercialization. There are several ways universities utilize IP, and Japanese corporations could be involved with5:
| [1] | Licensing to external companies (i.e. university owns IP, Japanese corporations pay for the IP usage) | |
| [2] | License assignment or selling/buying the IP (i.e. IP’s ownership is sold to third party) | |
| [3] | Create a spin-off company to utilize the IP (different to licensing, as spin-offs generally act as an extension of the university as explained in the Part II article) |
Methods [1] and [2] are straightforward in concept. However, spin-offs can involve Japanese corporations co-establishing the spin-off, also known as “Joint Venture Spin-off / Spin-out” or JVSO. While not uncommon, JVSO offer practical advantages. The industry partner becomes a part-owner and can influence the entrepreneurial mindset and commercial direction of the spin-off. It could also benefit the venture’s credibility and stability with the support of the industry partner too6.
These are just a few examples of how to engage and partner with universities or research institutes. The most suitable method will depend on each partnership’s objectives, timing and situation.
In this article series, we have covered the bottlenecks on the Japanese and Australian sides, and explored various forms of engagement or partnership the two parties can action. But it is important to note that there is a critical gap to be addressed for innovation to reach the real-world, this is commonly known as the “Innovation Valley of Death” (hereafter Valley of Death).
The Valley of Death refers to the timing where public funding (i.e. university funds) for research decreases, but there isn’t enough private fundings (i.e. industry partner support) to reach the minimum investment level needed to sustain the initiative7.
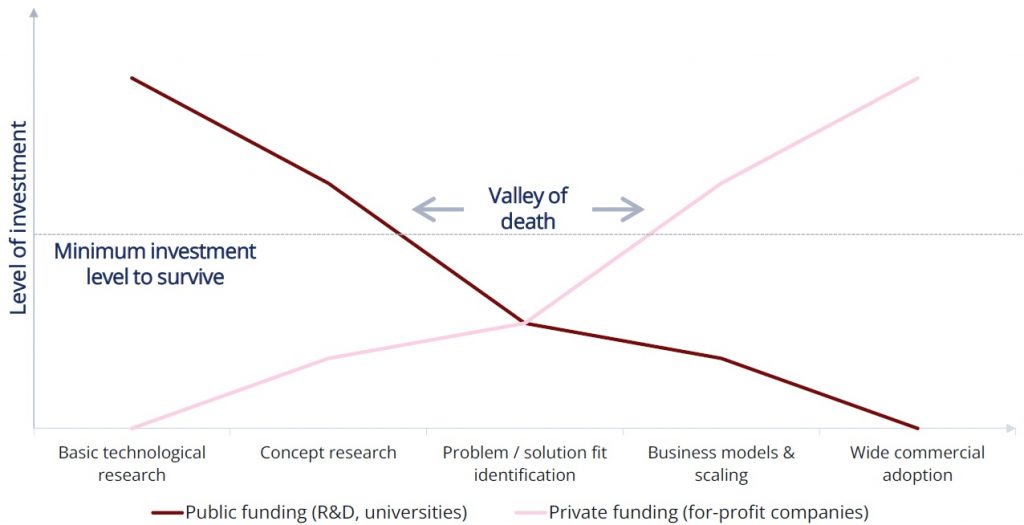
Graph 1: Idea to Value – The Innovation Valley of Death8
Here is a simple scenario to illustrate the Valley of Death:
| 1 | An innovative technology, heavily supported by university on the primary R&D funding, reaches the point where it is proven in a lab environment | |
| 2 | The next step is to test it in the real-world and investigate the problem/solution fit | |
| 3 | At this point, primary research funding from the university starts to diminish as the project nears its conclusion | |
| 4 | But industry players are not ready to invest due to uncertainty about the technology’s business scalability | |
| 5 | As a result, the funding/investment level may be insufficient to support the technology’s commercialization |
The above is an example where R&D is run by a separate entity (i.e. university). However, the same principle applies to internal corporate R&D and new business creation cases as well. For example, the initial R&D might be conducted, but further for scaling could be withheld due to core the business being prioritized or facing challenges that require those funds.
Also, it is noted that Australia is experiencing “publishing inflation”, where researchers are prioritizing the number of papers published over the impact of that paper/research9. This suggests an entrepreneurial mindset focused on commercialization might be lacking or not prioritized. While university professors and TTOs are aware of this issue and working to address it, change cannot happen overnight.
Despite these challenges, it is critical to outline that a smooth transition from the R&D to scaling / commercialization, enabled by sufficient collaborative funding or support is a vital requirement for any innovation to succeed.
For specific/apt Australian innovations that may appeal to Japanese corporations – to avoid the Valley of Death, several factors are crucial. The “Why?”, “What?” and “How?” of the Australian innovation must be (i) well-defined within an international context and (ii) discovered and identified by the right audience (e.g. Japan Inc.) and (iii) aligned with the right market situation and timing. And this is where IGPI Group can add value.
IGPI Group has been working with universities and corporations in Japan to address this issue of innovation commercialization by setting up a subsidiary entity “Advanced Technology Acceleration Corporation”, in short ATAC.
ATAC’s focus is being the bridge to support universities and research institutes, start-ups and Japanese corporations to perform hands-on incubation of cutting-edge technologies, bringing them to the real world based on market needs.
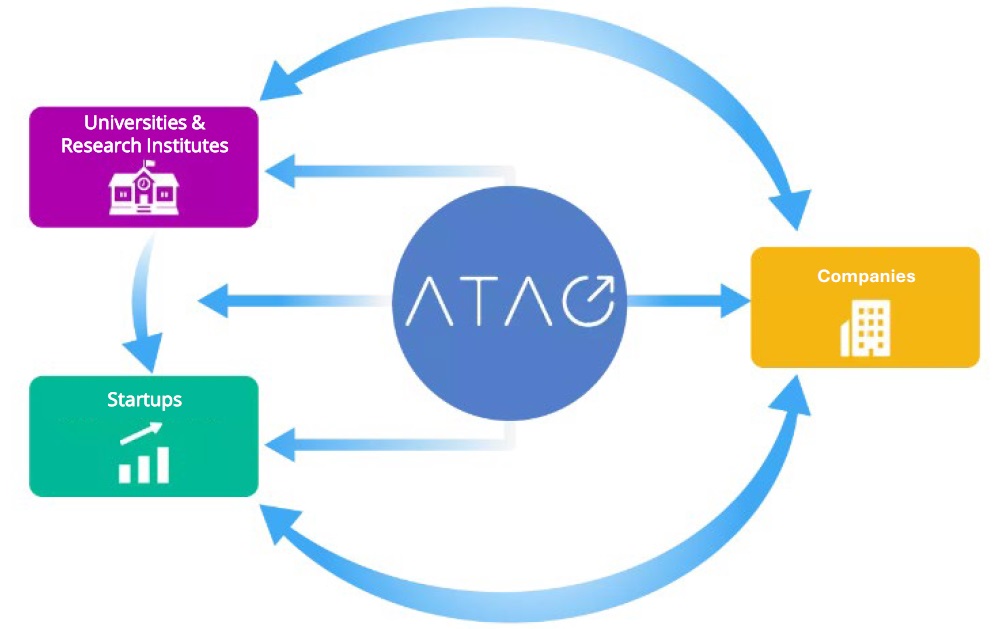
Figure 1: Diagram on ATAC’s support10
So far, IGPI Group has executed these initiatives for both Japanese corporations or individual Japanese universities. One example is a joint initiative with Toyota Motor Corporation to establish the “Innovative Technology Acceleration Platform” or ITAP, which collaborates with University of Tokyo’s School of Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology and Nagoya University on technology incubation11.
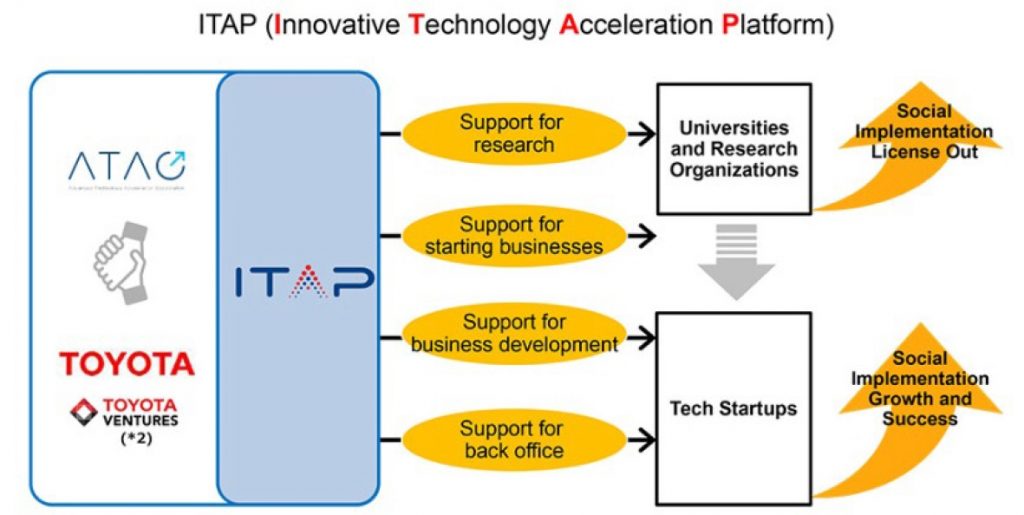
Figure 2: Toyota Global Newsroom12
Another example is a joint initiative with Nagoya Institute of Technology called “Nagoya Institute of Technology Expansion Platform” or NITEP, which specializes in incubating and commercializing the university’s expertise13.
These are just a few examples from Japan, but symbolizes a strong commitment to hands-on incubation and bringing innovation beyond the labs and to the real world through collaboration—literally “Bridge the Valley of Death”. IGPI Group has developed a deep-rooted understanding of innovation ecosystem and incubation processes and we see strong potential for applying our learnings in the Australia-Japan corridor too.
If you are an Australian university or research institute or an Australia corporation that has the ambition of building new businesses through Australia-Japan innovation, we will be glad to have a confidential conversation. IGPI provides highly customized business advisory to its diverse range of clients, including but not limited to:
I. Building your “for Japan” or “with Japan” strategy
II. Capability statement prioritization based on needs/wants of Japan Inc.
III. Market assessment for specific research initiatives x Japan as a market or Japan Inc.
IV. Strategic partner/capabilities search x Japan
V. Commercial negotiations support
VI. Other custom hands-on support (for/in Japan) etc.
To find out more about how IGPI Group can provide support for businesses, browse through our insight articles or get in contact with us.
1 Knowledge Commercialisation Australasia – https://techtransfer.org.au/ipc-training/commercialisation/who-participates-in-commercialising-universities-ip/
2 University of Melbourne Contract research – https://research.unimelb.edu.au/partnerships/collaborate/research-collaboration/contract-research
3 Catalant Everything you need to know about CoE – https://catalant.com/coe-everything-you-need-to-know-about-centers-of-excellence/
4 The University of Queensland – https://smp.uq.edu.au/research/research-centres/arc-centre-excellence-quantum-biotechnology
5 Knowledge Commercialisation Australasia – https://techtransfer.org.au/ipc-training/commercialisation/commercialisation-pathways-and-vehicles/
6 J-Stage Articles – https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jsmeicbtt/2002.1/0/2002.1_77/_article/-char/en
7 Idea to Value – https://www.ideatovalue.com/inno/nickskillicorn/2021/05/the-innovation-valley-of-death/
8 Idea to Value – https://www.ideatovalue.com/inno/nickskillicorn/2021/05/the-innovation-valley-of-death/
9 The Age: We’ve hit peak science, and that’s not good https://www.theage.com.au/national/we-ve-hit-peak-science-and-that-s-not-good-20240116-p5exkb.htmll
10 ATAC website – https://igpi-atac.co.jp/
11 Toyota Global Newsroom – https://global.toyota/en/newsroom/corporate/37000298.html
12 Toyota Global Newsroom – https://global.toyota/en/newsroom/corporate/37000298.html
13 IGPI News – https://www.igpi.co.jp/2020/07/28/news_20200728/

Mr. Rachit Khosla is the Country Manager of IGPI Australia. Rachit is a seasoned strategy consulting professional with over 14 years of experience in leading and executing market entry and growth strategies (both organic and inorganic) and open innovation engagements for Fortune 500 businesses and large MNCs across the Asia Pacific. He has advised clients in a diverse range of industries, including automotive, fin-tech, industrial and manufacturing, med-tech & healthcare, smart cities, construction materials, travel, IT & telecommunications to name a few. Rachit was the former Country Manager and Director for YCP Solidiance (now Japanese-owned) and Founder and CEO of an online B2B marketplace startup for professional advisory services focused on Emerging Markets.

Mr. Kaoru Shingae is a Consultant at IGPI Australia. Prior to joining IGPI, Kaoru worked at Toyota, BMW and Boston Consulting Group, primarily specializing in the Automotive and Mobility sector and with exposure to wider industrial sectors. Kaoru has both internal and external strategy experience with a deep understanding on ‘What’ is most important for all stakeholder’s future. He has end-to-end experience from corporate and enterprise-level planning to all the way down to operational planning. Kaoru is a holistic all-rounder who engages with both strategic and operational stakeholders throughout the company. Past achievements include crisis turnaround plans, long and mid-term vision plans, CEO’s company goal plans and sales & market operational plans plus delivery, to name a few. Kaoru has graduated from The University of Melbourne with a Bachelor of Commerce.
Ms. Devina Hashifah is an Intern at IGPI Australia (Nov 2023 – Feb 2024). Devina graduated with a Bachelor of Commerce from the University of Melbourne, majoring in Marketing and Management. She has previously worked in the financial advisory sector and student consulting organizations, conducting research for clients from the agriculture, renewable energy, microfinance, and media industry.
IGPI Group is a Japan rooted premium management consulting & Investment Group headquartered in Tokyo with a footprint in Osaka, Singapore, Hanoi, Shanghai & Melbourne, as well as parts of Europe and India. The organization was established in 2007 by former members of the Industrial Revitalization Corporation of Japan (IRCJ), a USD 100 billion sovereign wealth fund focusing on turn-around projects in Japan. IGPI Group has 13 institutional investors, including Nomura Holdings, SMBC, KDDI, Recruit & Sumitomo Corporation to name a few. IGPI Group has vast experience in supporting Fortune 500s, Govt. agencies, Universities, SMEs and funded startups across Asia and beyond for their strategic business needs and hands-on support across a wide variety of industries. IGPI group has ~8,500 employees on a consolidated basis.
* This material is intended merely for reference purposes based on our experience and is not intended to be comprehensive and does not constitute as advice. Information contained in this material has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but IGPI does not represent or warrant the quality, completeness, and accuracy of such information. All rights reserved by IGPI.